FAQ
Where is the mailing list?
It seems we’ve hidden the link to our mailing lists a bit too well.
We have two mailing lists:
- Asterisk-Java Users for users of Asterisk-Java seeking help
- Asterisk-Java Users for developers of Asterisk-Java, i.e. the guys enhancing the library code itself. This list not intended to provide support regarding the use of Asterisk-Java.
Professional services around asterisk-java, java and telephony in general is available from trion.
What are the different components I can use to integrate my application with Asterisk? Which one should I choose for my particular task?
| AMI | AGI | IAX | C Module | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Make/redirect calls | x | - | x | x |
| Query active calls | x | - | - | x |
| Query extension status | x | - | - | x |
| Stop/start recording | x | x | - | x |
| Receive/send media | - | - | x | x |
| Modify/add dialplan | x | - | - | x |
| Act as IVR | - | x | - | x |
| Act as soft phone | - | - | x | x |
| Act as endpoint/caller | - | x | x | x |
| Click to call | x | - | - | - |
| Dashboard/status | x | - | - | x |
How do I produce trace files that be sent to the mailing list for help?
We recommend you use NetCat (http://netcat.sourceforge.net/) or Wireshark (http://www.wireshark.org/). Wireshark is a better option for less technically adept users. Either way, we need a capture of the conversation between your program and the Asterisk server, and we’d also like the output from Asterisk-Java’s logging. Furthermore, it usually helps to see the source in order to follow what we’re seeing in the traces.
How can I track a call I’ve originated through the Manager interface?
With the Live API, you can use the originateToXXXAsync methods in org.asteriskjava.live.DefaultAsteriskServer and provide a unique call-back for your originates. When initiating a call using the Manager API and the Originate command, set a variable on that call. Then track the events the Manager API emits, if you encounter a NewChannelEvent get the variable from that channel and match it to a call. From there on you can use the channel name to track events.
How do I disable the debug or “INFO” output from asterisk-java?
Asterisk-Java uses commons-logging and log4j (http://logging.apache.org/log4j/docs/) so you can easily configure what kind of messages you want to log and where the messages should be written to. If you configure log4j to the OFF level for Asterisk-Java classes, you should get the behavior you are looking for. Basically there are two options: By default commons-logging uses java.util logging so you can have a look at the JDK documentation on how to configure it. The second option is to put a log4j.jar on your classpath along with a log4j.properties file to configure it.
How do I prevent Asterisk-Java from deadlocking when I fire actions in response to a received event?
Asterisk-Java dispatches events to your classes on an event-dispatch thread. You must use the Live API or send actions on another thread if you don’t want actions to block incoming events.
Can I send media or files through Manager interface?
Currently, there is no support for sending media or files across the Manager interface or the Gateway interface. Having access to the media stream without participating in the call would require saving it to a file or modifications to Asterisk itself, and you can expose any files (media or otherwise) through some other means (HTTP, SSH, etc).
Does Asterisk-Java work with Java 6? Java 5?
Asterisk-Java does work with Java 6. Stefan has used it while running Java 6 and 7 for development, and Martin uses Asterisk-Java inside a JBoss service bean all running under Java 6. Asterisk-Java currently supports Java 5 as well, and all source should remain 1.5-compatible for the time being.
Can I use Asterisk-Java with AstMan Proxy?
AstMan proxy requires some modifications in order to be successfully used with Asterisk-Java. Gaetan Minet has created a patch to AstMan Proxy that he has offered for download, with some documentation, at http://dev.mcit.be/various/astmanproxy-asterisk-java.html.
As of AstManProxy 1.23 most of the issues have been fixed and the patch is no longer required. You will not be able to use the CommandAction however as AstManProxy currently converts all NL characters to CR/NL. This issue still has to be fixed by AstManProxy in a future version.
What are some ways of securing an AGI script?
The FastAGI protocol itself has no support for authentication and encryption. You can add authentication at the application level using username and password parameters and verifying those. For encryption you have to revert to a VPN or other network-layer solutions. You could also consider writing a FastAGI ‘proxy’ which sits on the Asterisk server so that the clear unauthenticated text is only transmitted locally. The proxy could then demand authentication/encryption using something like SOAP to the actual end point.
Can I have an example of using an AGI server in a container like JBoss?
Yes. Here’s a JBoss EJB3 MBean that creates and destroys an AGI server.
@Depends({"JNDI name of anything your Agi scripts depend on"})
@Management(AgiManagement.class)
@Service
public class AgiMBean implements AgiManagement
{
private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(AgiMBean.class);
private AgiServerThread agiServerThread = null;
class AgiServerThread extends Thread implements Runnable
{
private AgiServer agiServer;
public AgiServerThread(AgiServer agiServer) { this.agiServer = agiServer; }
public void run()
{
try
{
agiServer.startup();
log.info("Asterisk Gatway Interface server MBean has been started");
} catch (IOException e) // NOPMD
{
// nothing we can do about that and exceptions have already been
// logged by startup().
log.trace("Exception from startUp(), probably already logged", e);
}
}
public AgiServer getAgiServer() { return agiServer; }
}
public void start() throws Exception
{
try
{
// get agi server & start it
DefaultAgiServer agiServer = new DefaultAgiServer();
agiServer.setMappingStrategy(new ClassNameMappingStrategy(false));
agiServerThread = new AgiServerThread(agiServer);
agiServerThread.start();
} catch (Exception ex)
{
log.error("Startup failed in MBean AgiMBean -- attempting to continue", ex);
}
}
/**
* Note that on JBoss 4.0.5, this method is accidentally called twice by JBoss. It is a known bug; reports can be found at:
* <p>
* http://jira.jboss.org/jira/browse/EJBTHREE-711<br/>
* http://jira.jboss.org/jira/browse/EJBTHREE-766<br/>
* http://jira.jboss.org/jira/browse/EJBTHREE-781<br/>
*/
public void stop() throws Exception
{
if (agiServerThread != null && agiServerThread.getAgiServer() != null)
{
agiServerThread.getAgiServer().shutdown();
}
}
}
public interface AgiManagement
{
public void start() throws Exception;
public void stop() throws Exception;
}
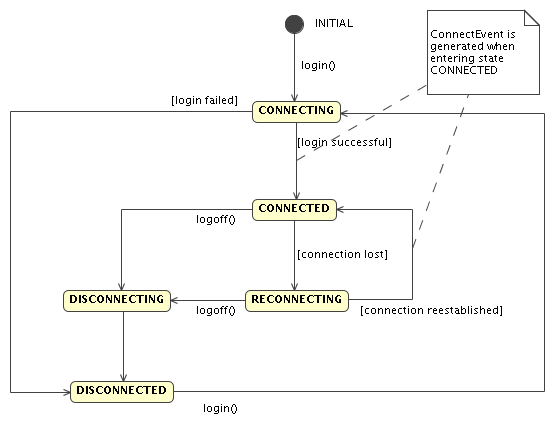
What happens when using the Manager API and Asterisk-Java loses the connection to Asterisk?
Asterisk-Java automatically reconnects if it looses the connection to Asterisk. Automatic reconnection attempts happens quite fast (with a 50 msec delay) for the first 10 attempts and at 5 seconds intervals later on. This is to make sure Asterisk-Java reconnects instantly when you reload Asterisk and does not consume too much resources for longer downtimes of Asterisk. Your application is notified of disconnects and reconnects by the two pseudo events DisconnectEvent and ConnectEvent so you can take appropriate action like clearing internal caches. By calling getState() on the ManagerConnection you can determine whether the connection is currently established or not and whether Asterisk-Java tries to reconnect.